Slow, inefficient linear motion systems lead to missed production targets, excessive wear, and costly downtime. Belt driven linear actuators provide a fast, reliable, and scalable solution. Discover why.
Belt driven linear actuators offer high-speed, long-stroke motion capabilities with low maintenance requirements. They are ideal for automation systems demanding rapid, precise positioning across a wide range of industrial applications.
Keep reading to understand features, specifications, and applications.
What Is Belt Driven Linear Actuators?
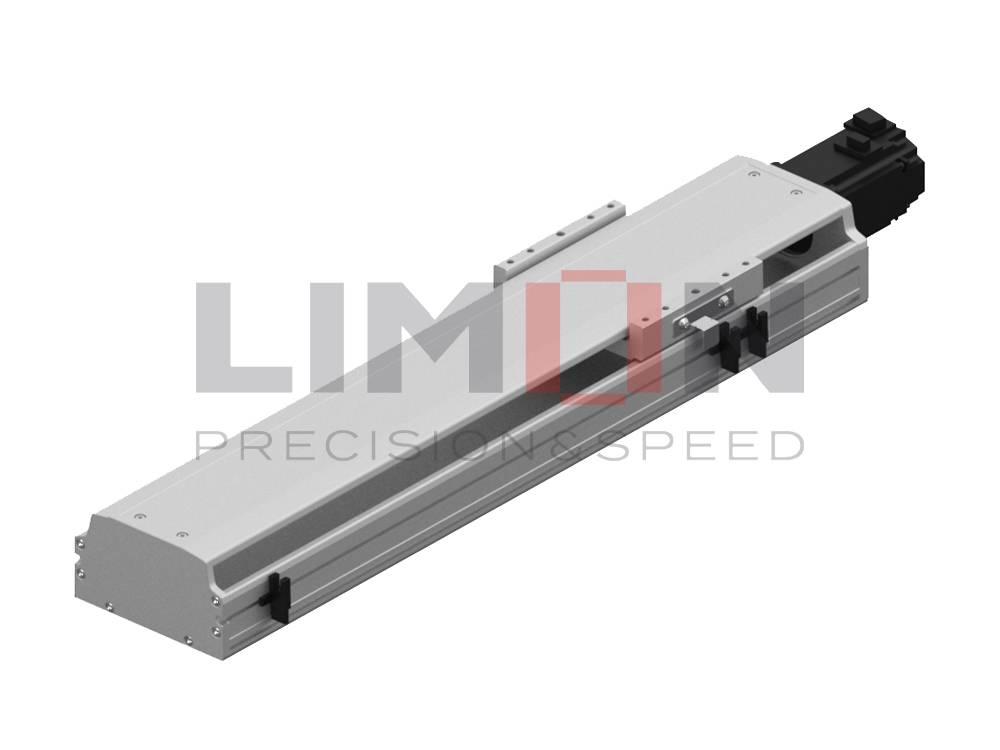
Belt driven linear actuators are mechanical devices that convert the rotary motion of a motor into precise linear motion through the use of a toothed belt and pulley system. Unlike ball screw actuators, which are optimized for precision and heavy loads over shorter distances, belt-driven systems are specifically engineered for high-speed, long-stroke, and lighter-load applications.
At their core, belt driven linear actuators consist of:
-
A motor connected to a drive pulley,
-
A toothed belt looped around a drive and an idler pulley,
-
A carriage attached to the belt that moves along a rigid frame,
-
Linear guideways supporting the carriage for smooth, stable travel.
The belt’s teeth engage with the pulley grooves, ensuring synchronized, slip-free movement. Because belts are flexible, actuators can achieve longer strokes than rigid screw-based systems without the risk of buckling or whip.
These systems are crucial in sectors like packaging, assembly automation, medical device manufacturing, material handling, and 3D printing, where speed and efficiency are paramount.

Features of Belt Driven Linear Actuators
Belt driven linear actuators come packed with features that make them ideal for dynamic and demanding environments:
1. High-Speed Motion
Capable of reaching speeds exceeding 5 meters per second, belt driven systems are significantly faster than screw-driven counterparts. They enable rapid cycle times for high-throughput applications.
2. Long Stroke Lengths
While ball screws are limited in practical length due to critical speed limitations, belt driven actuators can achieve strokes over 6 meters or more without performance loss.
3. Low Maintenance
The flexible belts are resistant to wear and do not require frequent lubrication. Modern belts with embedded steel or Kevlar reinforcement provide excellent service life with minimal upkeep.
4. Lightweight and Compact Design
The use of belts and aluminum frames results in a lightweight solution without sacrificing structural rigidity, making it suitable for integration into robotic arms, gantries, and mobile platforms.
5. Quiet Operation
Compared to chain drives or rack-and-pinion systems, belt drives produce less noise and vibration, an important feature in noise-sensitive environments like medical device assembly.
6. Versatile Mounting Options
These actuators offer multiple mounting configurations, whether horizontally, vertically, or inverted, allowing for flexible system design.
These features make belt driven linear actuators a popular choice where speed, simplicity, and cost-efficiency are critical.
Advantages of Belt Driven Linear Actuators
The use of belt driven linear actuators offers distinct advantages that help optimize industrial and automation processes:
1. Speed and Responsiveness
Because of their low mass and low inertia, belt-driven systems can accelerate and decelerate very quickly, improving overall system throughput and efficiency.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Belt driven linear actuators are generally more affordable than comparable ball screw systems, especially for long travel lengths, reducing both initial investment and total cost of ownership.
3. Reduced Risk of Screw Whip
Unlike long ball screws, which can experience vibration (“whip”) at high speeds, belts maintain stable performance even at extended lengths and high velocities.
4. Simple Construction
The mechanical simplicity of belt actuators results in fewer components, reducing potential points of failure and simplifying assembly and maintenance procedures.
5. Energy Efficiency
Lower friction and mass translate to reduced energy consumption, allowing smaller, more economical motors to achieve desired performance levels.
6. Clean Operation
Belt systems produce fewer particles and require less lubrication, making them suitable for cleanroom environments or sensitive manufacturing processes.
In dynamic applications where rapid positioning and minimal downtime are vital, belt driven linear actuators provide outstanding value and performance.
Specifications for Belt Driven Linear Actuators
When selecting belt driven linear actuators, several critical specifications must be considered to ensure optimal performance:
1. Stroke Length
Determine the required travel distance. Belt actuators can easily accommodate custom stroke lengths beyond standard sizes, up to 10 meters or more.
2. Speed and Acceleration
Depending on application needs, actuators should offer speeds from 2 to 5 meters per second and acceleration rates above 10 m/s² for high-cycle operations.
3. Load Capacity
Assess the static and dynamic load ratings, including moment loads (pitch, yaw, and roll moments). Belt driven actuators typically support medium loads—perfect for conveyors, gantries, and positioning stages.
4. Repeatability and Accuracy
While ball screws offer micron-level accuracy, belt actuators typically achieve repeatability within ±0.05 mm to ±0.1 mm—sufficient for many automation tasks.
5. Belt Material and Construction
Belts made from polyurethane with steel or Kevlar cords provide durability, reduced stretch, and longer lifespan.
6. Guideway Type
Linear guideways ensure smooth motion and support loads in multiple directions. Choose between single or double rail systems based on rigidity requirements.
7. Motor Compatibility
Belt driven actuators are typically compatible with stepper motors, servo motors, or integrated motor-drive systems, depending on performance and control needs.
By carefully matching these specifications to project requirements, users can ensure maximum reliability and productivity from their belt driven linear actuator systems.
Application of Belt Driven Linear Actuators
Belt driven linear actuators serve a wide array of industries and applications thanks to their versatility, speed, and cost-efficiency:
1. Packaging and Material Handling
High-speed conveyor belts, pick-and-place arms, and carton filling systems rely on belt actuators for fast, repeatable motion across extended distances.
2. Robotics and Automation
Belt actuators form the linear axes in multi-axis robotic gantries, offering lightweight, fast, and accurate movement ideal for assembly and inspection tasks.
3. 3D Printing and Laser Cutting
Large-format 3D printers and laser cutters often use belt-driven X and Y axes to achieve quick, smooth movements over large build areas.
4. Medical Device Manufacturing
Cleanroom-compatible belt actuators enable fast material transport and precise component handling in medical equipment production lines.
5. Semiconductor and Electronics
In wafer handling, PCB assembly, and automated inspection, belt actuators provide clean, accurate linear motion without contamination risks.
6. Photovoltaic and LCD Production
Large-panel manufacturing benefits from long-stroke, high-speed belt systems that maintain consistent, vibration-free movement over oversized surfaces.
From lightweight desktop machines to heavy-duty industrial automation lines, belt driven linear actuators continue to redefine possibilities for high-performance motion systems.
Summary
Belt driven linear actuators offer fast, efficient, and scalable motion solutions—perfect for automation, material handling, and dynamic manufacturing environments.For further questions please contact [email protected]


_1.jpg)