Linear guides play a crucial role in various industries, serving as essential components in machinery and equipment. Whether you are a seasoned engineer or a novice exploring the world of mechanical systems, understanding what linear guides are and how they function is fundamental. In this article, we will delve into the basics of linear guides, their types, applications, and why they are indispensable in the modern manufacturing landscape.
What Are Linear Guides?
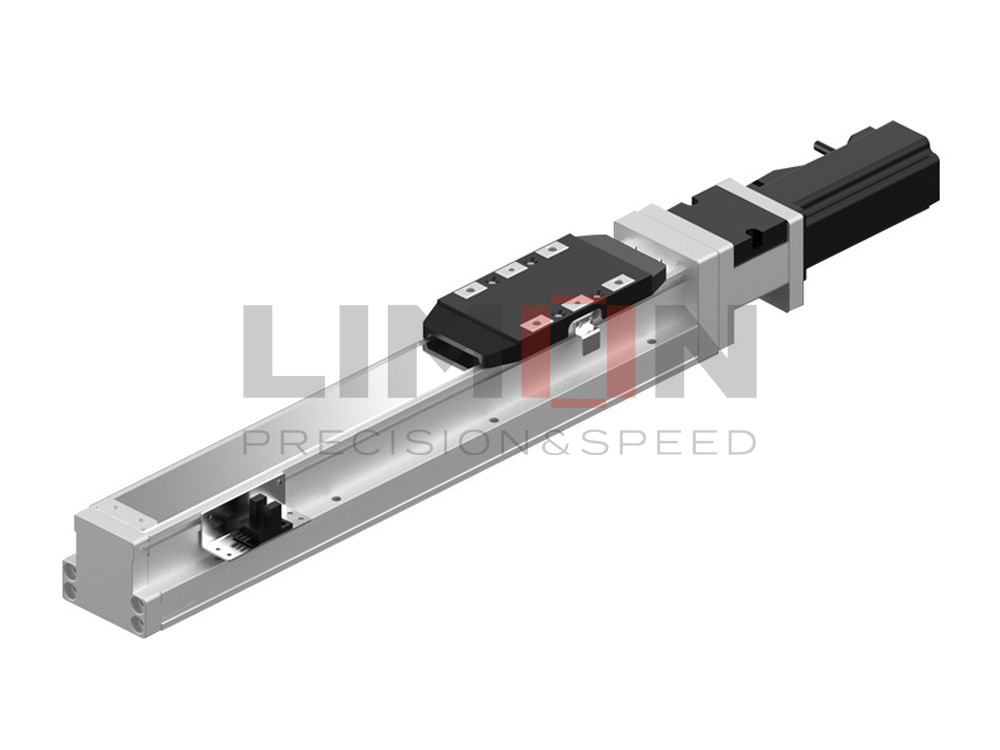
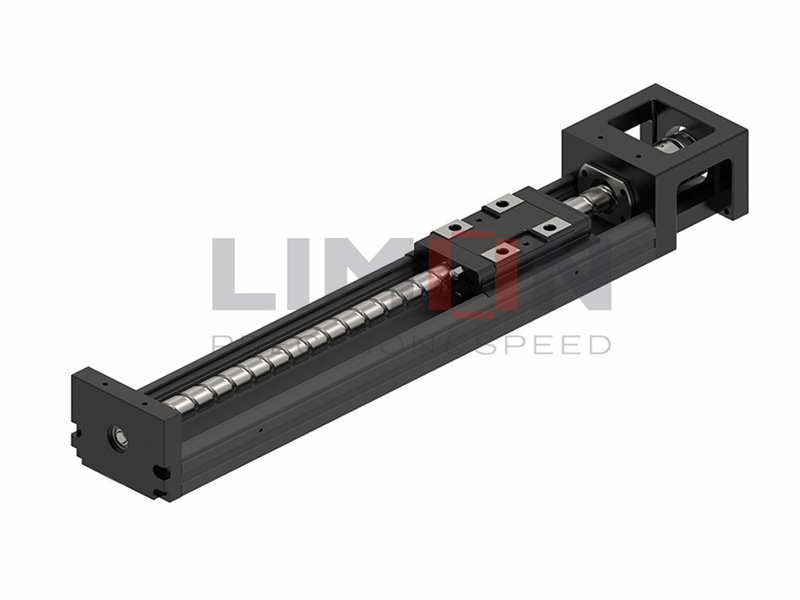
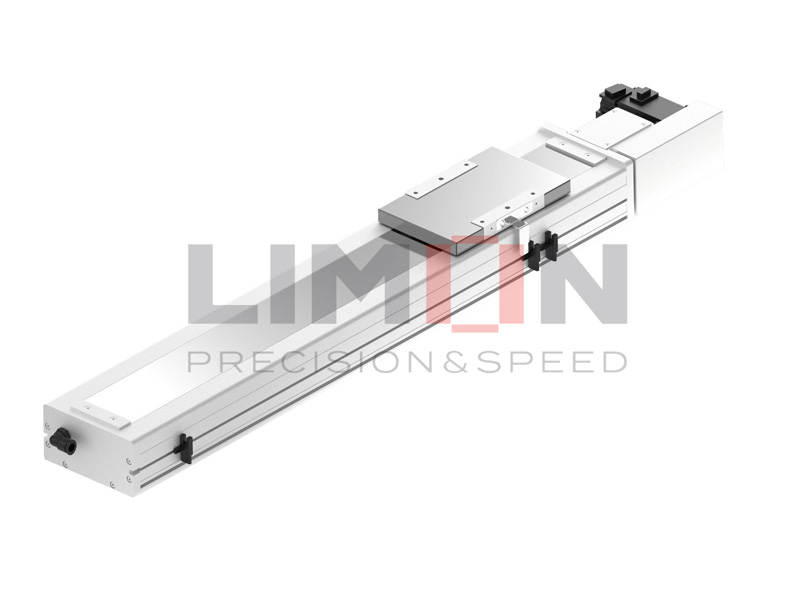
Linear guides, also known as linear motion guides or linear bearings, are mechanical systems designed to facilitate smooth and precise linear motion in a single direction. They are commonly used in conjunction with machine elements such as slides, rails, and carriages to enable controlled movement along a fixed path. Linear guides eliminate friction and provide stability, ensuring accuracy in various applications.
Types of Linear Guides
1. Ball Bearing Linear Guides:
Utilize ball bearings for reduced friction.
Well-suited for high precision and high-speed applications.
Commonly used in industries such as automation, robotics, and CNC machining.
2. Roller Bearing Linear Guides:
Employ cylindrical rollers for motion.
Suitable for heavier loads and harsh environments.
Widely used in heavy machinery, manufacturing, and transportation systems.
3. Plain Bearing Linear Guides:
Lack rolling elements and operate using sliding friction.
Ideal for applications with lighter loads and where low friction is acceptable.
Found in cost-sensitive applications and DIY projects.
Applications of Linear Guides
1. CNC Machining:
Linear guides provide the precision and stability required for cutting, milling, and drilling processes.
2. Automation and Robotics:
Essential for precise movement in robotic arms, conveyor systems, and automated manufacturing processes.
3. Medical Equipment:
Used in devices like medical imaging equipment and robotic surgery systems for accurate positioning.
4. Aerospace and Defense:
Employed in aircraft and defense systems for reliable and controlled linear motion.
5. Packaging and Material Handling:
Linear guides play a vital role in packaging machinery and conveyor systems.
Advantages of Linear Guides
- Precision:Enable high levels of accuracy in various applications.
- Stability:Provide stability even in high-speed and heavy-load scenarios.
- Durability:Constructed with materials and designs to withstand harsh conditions.
- Smooth Operation:Offer smooth and consistent linear motion for improved performance.
- Reduced Friction:Minimize friction, enhancing efficiency and reducing wear and tear.
In summary, linear guides are integral components in numerous industries, contributing to the efficiency and accuracy of various mechanical systems. Whether you are working in manufacturing, automation, or any other field requiring controlled linear motion, understanding the types, components, and applications of linear guides is essential for successful design and implementation.